2025 Trend Insight for Fashion Sustainability
 2023-08-07
2023-08-07

 Sansansun
Sansansun

In 2025, the fashion industry is undergoing profound changes, encompassing a comprehensive transformation in procurement, production, sales, transportation, and usage patterns. The concept of global sustainable development requires considering the lifespan of products during the initial design phase and exploring how to integrate sustainable innovation. In the stage of material selection, sustainable measures emphasize choosing fiber materials that require less water and pesticides or utilizing fiber materials derived from agricultural by-products, as well as utilizing recyclable waste textiles or leather scraps. Another key stage occurs during the transformation, dyeing, and finishing processes, where sustainable apparel manufacturers play a crucial role in determining product characteristics, ensuring low-chemical impact solutions, and promoting environmentally friendly practices. Meanwhile, packaging also plays a significant role, particularly in selecting sustainability-oriented packaging components. At each stage, choosing packaging, transportation, and distribution methods that align with sustainable development commitments is a crucial step.
This report analyzes innovative environmentally friendly production technologies and performance characteristics in three parts: materials, production, and certification, based on the perspective of sustainable development. It explores the efforts and contributions of sustainable apparel manufacturers in driving the fashion industry towards a more sustainable future.

Eco-friendly Materials
In order to alleviate the degradation of soil and reduce the impact on biodiversity, an intensive farming approach is employed, utilizing materials from textile waste or agricultural and food industry waste. Additionally, an increasing number of material solutions are being developed to better predict the lifespan of products and select ingredients that facilitate recycling or biodegradation.
It is worth mentioning that in this season, we have also witnessed the broad application of protective materials extracted from traceable renewable resources, and the diversity of climate-friendly wool continues to expand, all while respecting animal welfare.
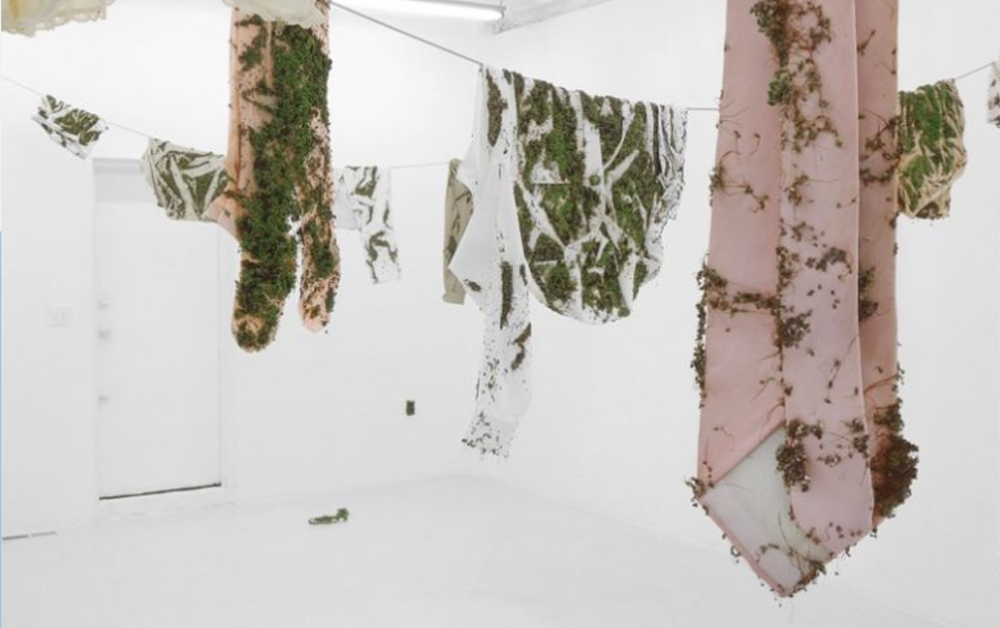

Eco-friendly Materials Recycling -- Regenerated Waste
Development Background:
Recycling has been established and is now moving toward a closed-loop production process.
Production Process:
1. Regenerating textile residues from wool, cotton, synthetic materials, or cellulose.
2. In addition to traditional mechanical recycling of wool and cotton, support is being given to chemical recycling of synthetic fibers and using cellulose residues or agricultural by-products, helping to alleviate the pressure on primary resources.
Performance:
Eco-organic, eco-recyclable, eco-traceable, eco-low chemical impact finishing
Application:
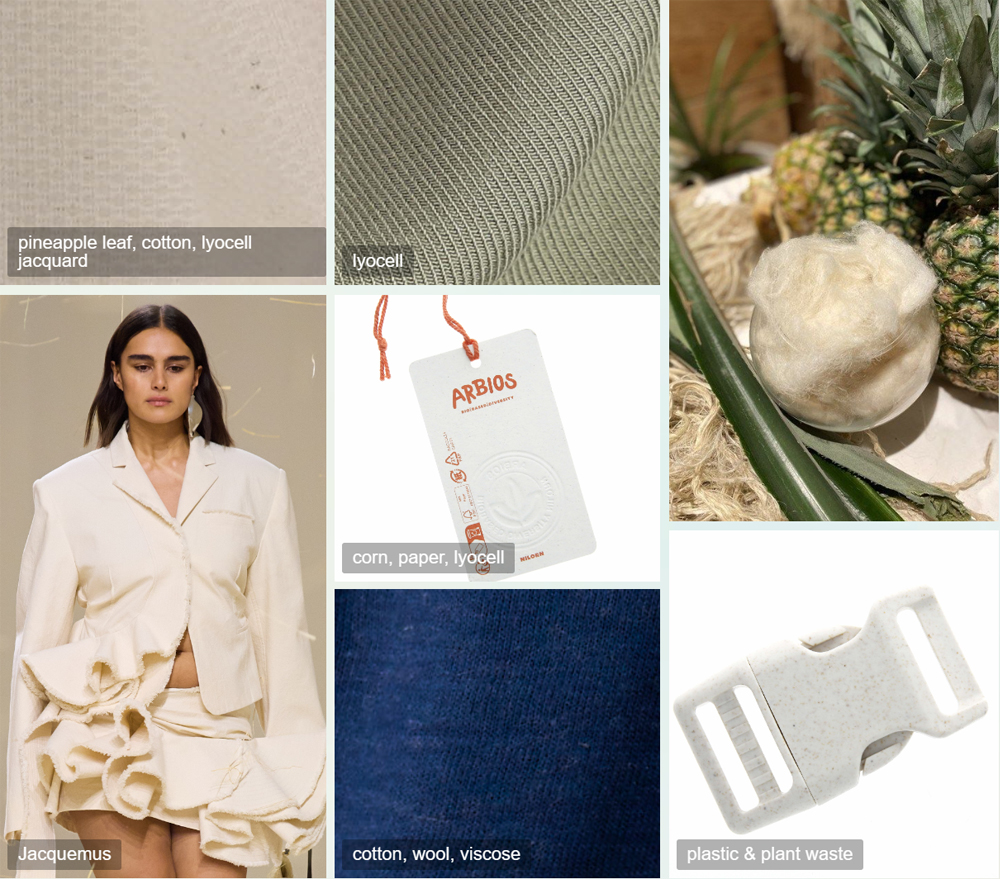
Knit & Woven: regenerated cellulose fibers such as Lyocell, viscose, pineapple leaf fibers extracted from agricultural waste, renewable fibers such as wool and cotton
Accessories: developing eco-functional components from agricultural waste plant residues, creating renewable/degradable tags from plant fibers such as corn stalks
Eco-friendly Materials Recycling -- Regenerated Materials
Development Background:
Developing new products through resource recycling and regeneration helps to address the increasingly severe resource and environmental crises.
Production Process:
1. Convert waste collected during ocean clean-ups into recycled polyester or polyamide, and optimize the synthetic materials to improve their degradability, thus minimizing the release of plastic microfibers into the environment.
2. Recycle and process used renewable products as secondary raw materials.
Performance:
Eco-recyclable, ecologically low chemical impact sorting
Application:
1. Knit & woven - recycled wool, recycled cotton, biodegradable Lyocell, recycled polyester, and recycled polyamide, etc.
2. Accessories - recycled paper, recycled silicone, recycled polyurethane, and recycled metal, etc.

Eco-friendly Materials Biological Sustainability -- Biobased Polymers
Development Background:
The products in today's fashion industry rely on two key raw materials: polyester and cotton. In order to overcome the dependence on fossil materials with high carbon emissions, bio-based polymers derived from renewable resources are favored.
Production Process:
1. Synthetic materials are transformed into bio-based polymers to make them ecologically degradable and reduce environmental pressure. 2. Develop new multifunctional materials from plant-based materials such as olive and mycelium waste. 3. Under suitable conditions, add specific additives to induce polymerization and reduce the decomposition time of the products.
Performance: Ecological bio-based polymers, ecological recycling, ecological traceability, ecological low chemical impact finishing.
Application:
Knit & Woven: bio-based polyamide, bio-based polyester, bio-based spandex.
Leather: use plant-based materials such as mycelium, fruit fertilizers, and algae to create bio-based leather.
Accessories: bio-based plastic accessories, bio-based polymer buttons, etc.

Eco-friendly Materials Biological Sustainability -- Bio-based Functional Finish
Development Background:
In order to enhance the sustainability of the product, improvements in functional processing and decorative finishes are also targeted towards recycling. Manufacturers are strengthening their creativity and researching functional bio-based materials that do not rely on fossil resources, in order to achieve 100% recyclability/degradability of the product, improve recycling efficiency, and reduce the product's carbon footprint.
Production Craft:
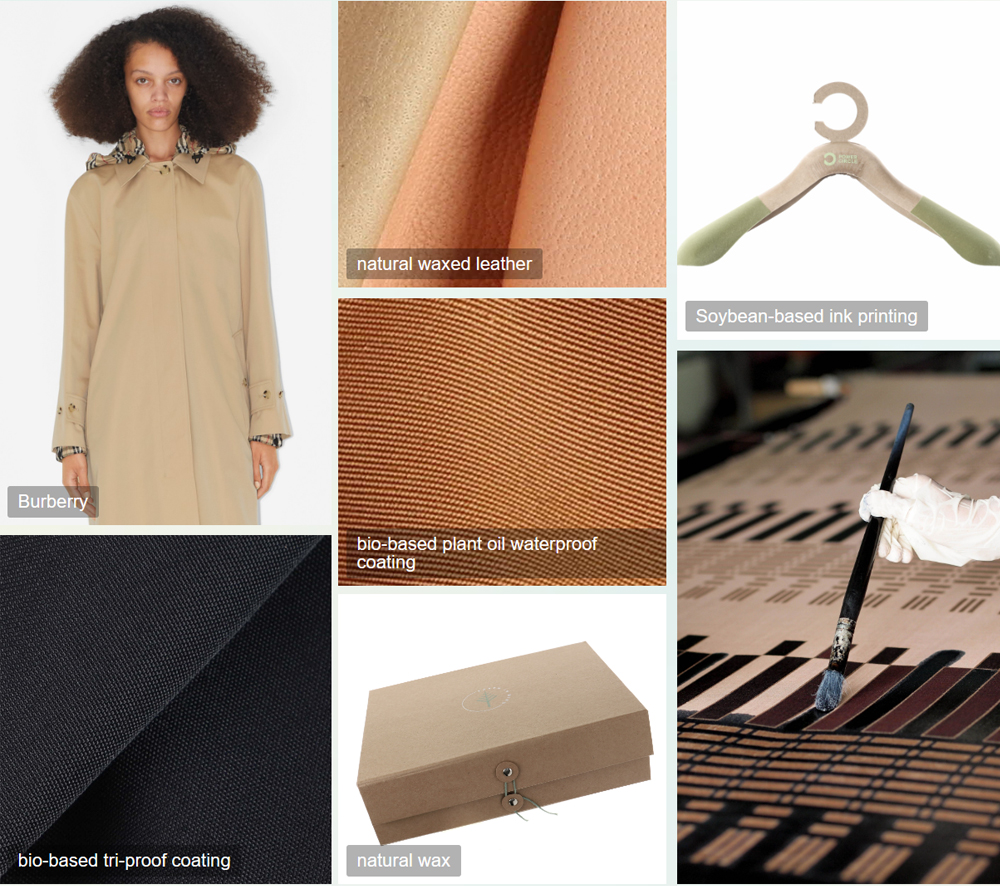
1. Development of bio-polymers for knitting, weaving, film, and coating, with properties such as cold resistance, wind resistance, and waterproofing, without the use of petrochemical products, specifically designed for outdoor applications. 2. Natural wax coatings or plant oil-based waterproof finishes. 3. Bio-based polyurethane for creating leather-like glossy finishes. 4. Alternatives based on high-resistance recycled paper and bio-based polymers, used for developing rain and moisture-resistant materials. 5. Gift boxes and hangers made without the use of glue, with natural wax finishes and soy-based inks replacing potential toxic additives.
Performance:
Breathable waterproofing, anti-pilling, easy maintenance, ecologically traceable, quick-drying, wind-resistant, eco-friendly bio-based polymers, eco-friendly low-chemical impact treatment.
Application:
Natural wax/plant oil waterproof finishes, bio-based functional coatings/films, plant-based inks.
Green Production
In textile production, an increasing number of manufacturers are actively promoting green production practices by choosing natural plant-based processing methods, such as plant dyes and plant tanning. Simultaneously, they adopt low-energy and high-efficiency technologies and equipment to reduce energy consumption and carbon emissions. Through these measures, efforts are made to minimize the negative environmental impacts of production and provide textile products that meet sustainable development requirements.
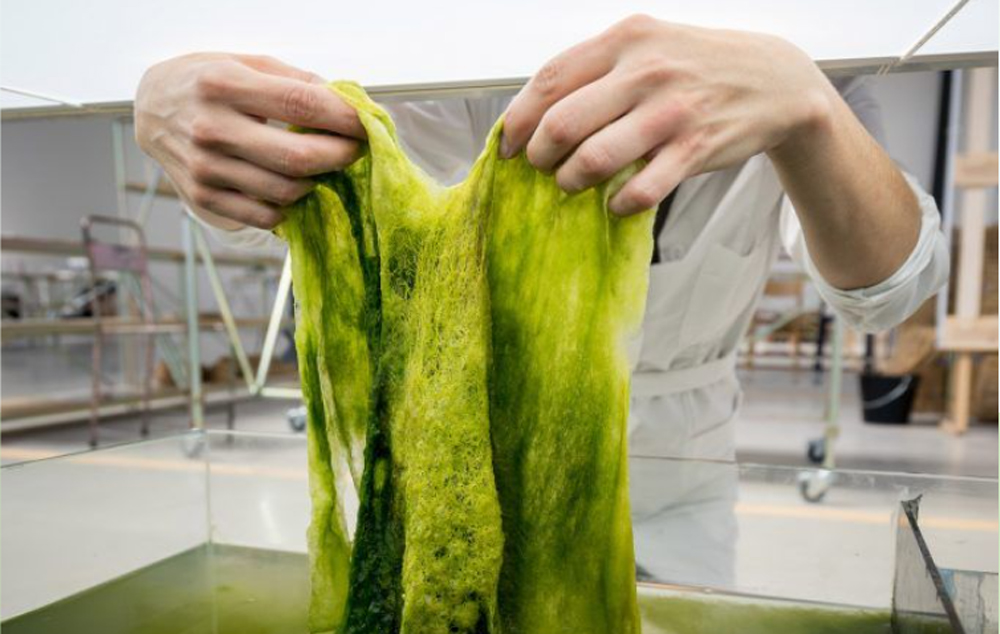

Green Production Bio-based Finish -- Natural Plant Dye
Development Background:
Aiming to implement the sustainability of the product lifecycle, one of the factors affecting the environmental impact in the production process is the dyeing and finishing process. By using plant-based materials to replace traditional chemical materials and reduce pollution, the goal is to make green transformation a reality.
Production Craft:
1. Development of high-performance pigment dyeing using plant residues such as wood
2. Fermentation dyeing using agricultural waste
3. Natural dyeing using plant-based pigments such as flowers
Performance:
Eco-friendly with low chemical impact and ecologically sustainable
Application:
Dyeing of yarn or fabric, producing environmentally friendly ribbons and labels using plant-dyed yarns

Green Production Bio-based Finish -- Plant Tanning
Development Background:
Leather quality is now being measured by its environmental performance, and the supply of chrome-free leather products is steadily growing. Synthetic metal-free tanning agents have been reformulated to minimize the content of formaldehyde, bisphenol F, and S. In addition, environmentally friendly vegetable tanning has received attention.
Production Process:
1. In vegetable tanning, the range of recycling tanning agents continues to expand with the use of lacquer tree in addition to olive. Vegetable tanning diversifies the range through bright tones that maintain their color without fading.
2. Research is based on synthetic plant extracts polymers to ensure product safety and contribute to resource recycling. Residues of hemp oil or olive leaves are used in the formulation to provide a soft, smooth, and flexible hand feel while ensuring efficient biodegradability.
Performance:
Eco-friendly - Low chemical impact finishing, eco-traceability, eco-waterless, easy care, eco-recycling
Application:
Shirts, jackets, coats, and other products

Green Production Low Consumption -- Minimalist Surface
Development Background:
By adopting low-chemical impact finishing technology that conforms to environmentally friendly and sustainable concepts, the dual goals of environmental friendliness and resource conservation have been successfully achieved. At the same time, this technology presents a more striking visual effect on the accessory finishes based on low consumption and environmental protection.
Production Craft:
1. PVD (Physical Vapor Deposition) precision processing is used to develop continuously changing mole patterned metallic finishes. Compared to traditional electroplating, this technology can form highly wear-resistant metallic coatings while minimizing the impact.
2. Mechanical finishing. Creating a careful gloss through wire drawing or satin polishing finishes. To showcase the beauty of recycled metals such as aluminum, brass, or recycled zinc alloy, the surface undergoes antiquing, etching, and hammering to randomly capture light.
Performance:
Ecological low-chemical impact finishing, ecological recycling.
Application:
Accessories requiring finishing for buttons, zippers, and tags.
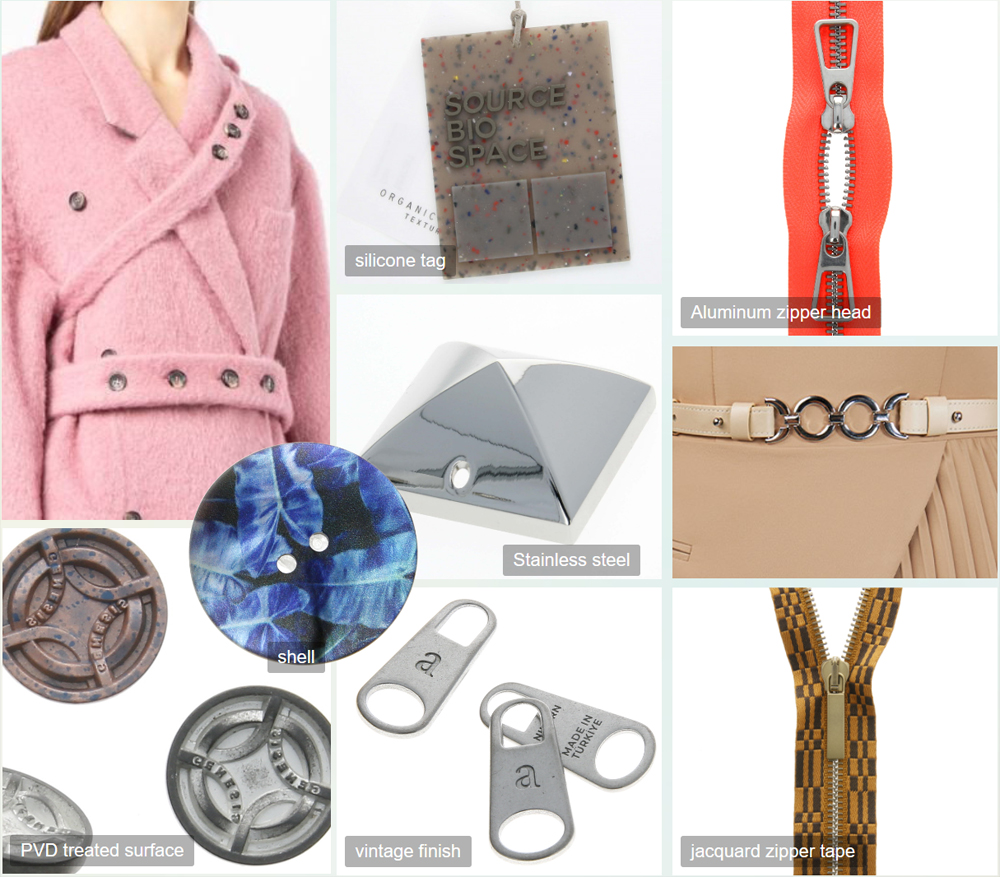

Excellence Certification
As global efforts for sustainable development continue to advance, an increasing number of domestic and international renowned brand businesses and associations are actively participating and formulating a series of certification standards to address challenges in environmental and social responsibility. The objectives of these certification standards are to encourage enterprises to adopt sustainable business practices, including reducing environmental impact, enhancing resource efficiency, promoting social justice, and protecting labor rights.
These standards not only require enterprises to comply strictly with relevant laws and regulations but also focus on the management of the entire product life cycle, supply chain traceability, and corporate social responsibility. Through certification, companies can demonstrate their proactive efforts and outstanding performance in sustainable development, thereby strengthening consumer trust and recognition towards their products.

Excellent Certification Lifecycle -- LCA
Introduction:
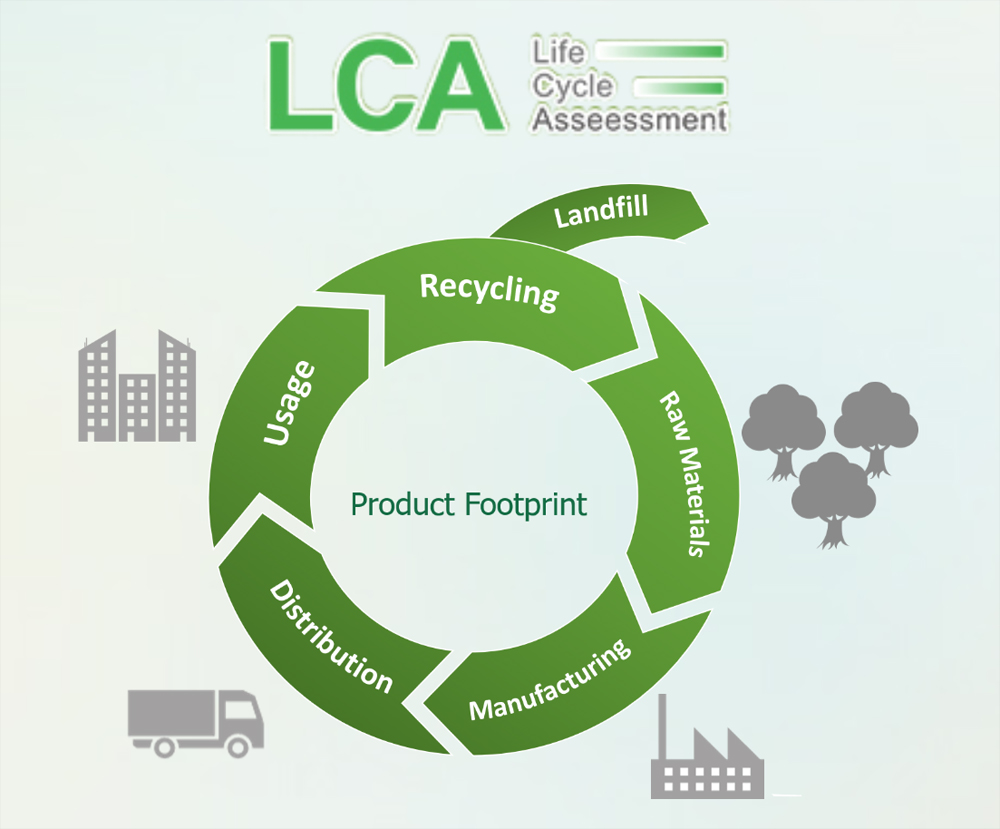
Life Cycle Assessment (LCA certification) is a method for evaluating the overall environmental impacts of a product or a category of facilities throughout the "cradle-to-grave" process, from a regional, national, and even global perspective, as well as the height of sustainable development. Therefore, by using LCA to assess various alternative solutions for different products or facilities, optimized solutions can be selected.
Evaluation criteria:
ISO 14040/44, defined by ISO as: a method for aggregating and evaluating the environmental impacts and potential impacts caused by all inputs and outputs in the life cycle of a product system.
LCA certification generally consists of four stages:
1. Determining the purpose and scope of analysis
2. Inventory analysis
3. Impact assessment
4. Life cycle interpretation.
Excellent Certification Trace Responsibility -- Source Standards
FSCThe certification of forest management by FSC is aimed at forest management units. It is a process conducted by independent third-party FSC forest certification bodies, according to established forest management standards and recognized principles and criteria, to assess the performance of forest management and demonstrate compliance with sustainable management requirements. Chain of custody certification ensures the identification of each production stage in the wood processing enterprises, including transportation and processing of timber, to guarantee that the final product originates from well-managed forests that have been certified.
RWS certification ensures five-star treatment for sheep on farms and ensures the best practices in land management and protection. Throughout the processing stages, the certification ensures the correct identification and traceability of wool from certified farms.
The purpose of GOTS (Global Organic Textile Standard) certification is to ensure organic status throughout the entire process, from the harvesting of raw materials to responsible processing and labeling, in order to provide trusted products to the end consumers. This standard covers the processing, manufacturing, packaging, labeling, trading, and distribution activities of textile products containing a minimum of 70% organic natural certified fiber content.

Excellent Certification Trace Responsibility -- Environmental Regeneration
Bluesign is a certification emblem in the textile industry related to environmental protection. It is a strict textile environmental standard certification promoted by the Swiss company Bluesign Technologies AG. It represents environmental safety throughout the entire production chain, including certifications for consumer safety, worker protection, and waste emission.
GRS is a comprehensive set of evaluation standards for recycled products, which includes the determination of the recycled content in the products, the traceability of recycled materials in the supply chain, quality control in the production process of recycled products, corporate social responsibility, environmental management, and the prohibition of certain chemicals. Companies that meet these criteria and have a recycled content of over 20% in their products can apply for GRS certification.
RCS certification is another standard for recycling (regeneration) introduced by the TE Textile Trading Organization in 2013, providing certification basis for products made from recycled materials.
RCS certification is applicable to products with a recycled material content between 5% and 100%.


 Inquire(
Inquire(
 HOME
HOME Easy & Free -- The Item Trend for Active Suit
Easy & Free -- The Item Trend for Active Suit  You May Also Like
You May Also Like






















 Tel
Tel
 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
 Email
Email
 Address
Address






