2025 Performance & Eco-Friendly Fabric Industry Insight - Macro Trends
 2023-06-01
2023-06-01

 Sansansun
Sansansun

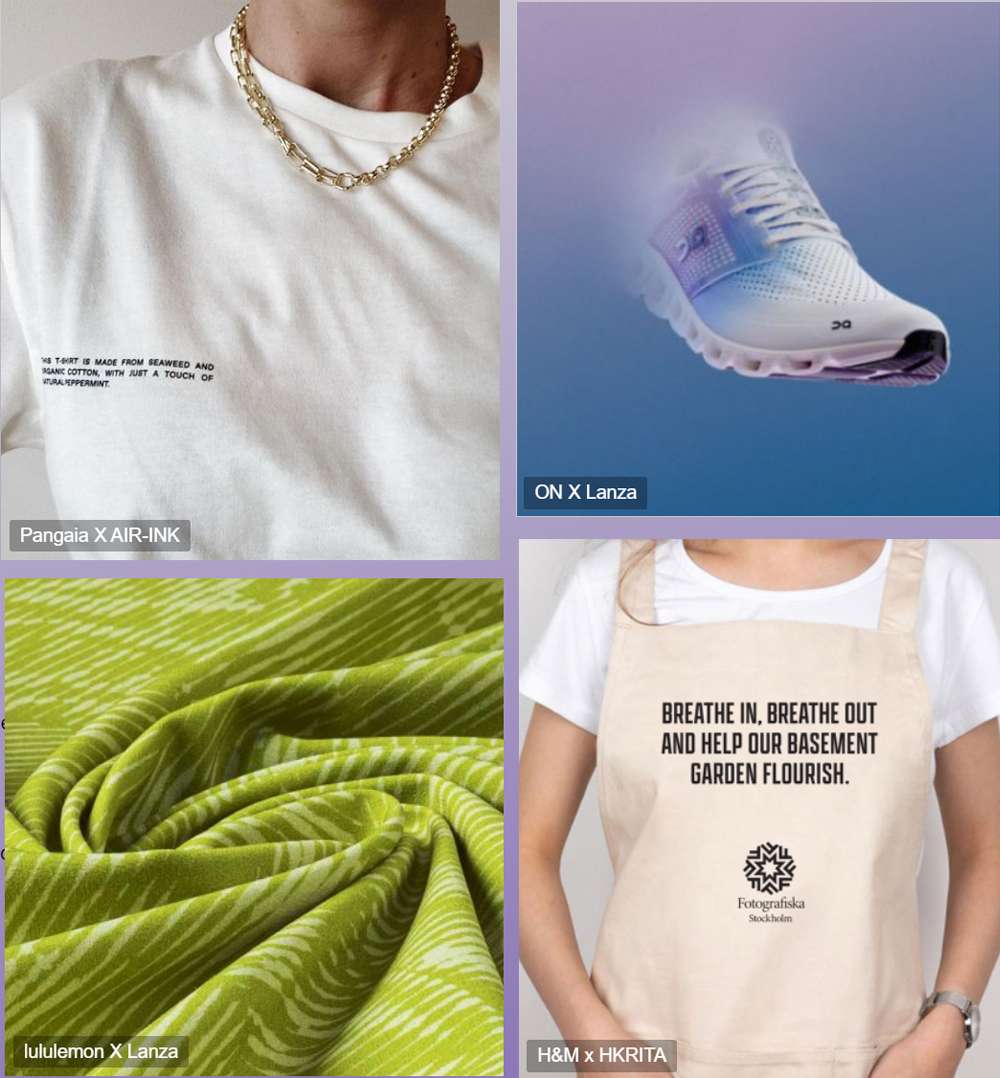
Bio-degradable
Degradable Polyester
Degradable Polyamide
Background
The fashion industry has been making efforts to reduce its impact on the natural environment by exploring various recycling and renewable technologies, as well as developing biodegradable synthetic materials. Although it has reduced the industry's impact on the environment and natural resources, the large amount of waste generated by the fashion industry remains a major source of environmental pollution. Therefore, the development of biodegradable technological materials is receiving increasing attention.
Application
1.The production technology for biodegradable polyester can currently meet the requirements for filling cotton, but it has not yet been applied to the weaving of fabrics for needle-based materials.
2.The current technology for biodegradable polyamide can meet the requirements for weaving needle-based fabrics, and the resulting clothing can quickly decompose under specific conditions in landfills.

Plant-based Materials
Plant-based Polyester
Plant-based Nylon
Plant-based Coating
Background
The textile industry has garnered global attention due to its significant carbon footprint, and ecological concerns have prompted a shift towards more environmentally sustainable plant-based materials, moving away from petroleum-based fibers.
Application
1.Plant-based fibers: Genomatica in the United States, Kaisai Biological in China, and Toray in Japan have invested in the development of plant-based nylon, while DuPont in the United States and Toray in Japan have invested in the development of bio-based polyester.
2.Huntsman, in partnership with Chemours, has created a new environmentally friendly finishing agent called Teflon EcoElite, which contains 63% plant-based materials, making it one of the first renewable sources of waterproofing in the industry. Compared to fluorination technology, it offers similar levels of performance, waterproofing, durability, and breathability.

Recycling
Post Consumer Textiles
Textile Offcut
Background
As an industry that is under strict scrutiny for its excessive use of natural and fossil resources, the fashion industry has been developing new materials through recycling technologies to reduce its impact on the environment. Prioritizing the use of recycled resources within the textile and clothing industry is currently an effective strategy to reduce its impact on resources and the environment.
Application
1.Mechanical recycling technology involves recovering wool or cotton fibers, as well as synthetic fibers, from post-consumer textiles or processing waste to produce recycled wool, cotton, and synthetic fibers. This process requires relatively high standards for recovered resources.
2.Chemical recycling technology has more development potential than mechanical recycling, but its environmental impact during production needs to be considered. Qingdao Amino Material Co., Ltd. in China has developed a new recycling technology that can recover elastic fibers intact, producing recycled fibers for continued use. This process is waterless and effectively reduces carbon emissions during production.

Carbon-negative Fabrics
Carbon Footprint Certification
Carbon Credits
Carbon Standards
Background
As "carbon neutrality" and "carbon peak" become national policies around the world, and monitoring of carbon emissions becomes increasingly strict, the development of zero-carbon products has become the future of sustainable development.
Application
1.Carbon capture technologies, such as using ink and paint made from recycled carbon dioxide, collecting pollution waste to cultivate bacteria for synthetic fiber production, and producing recyclable textiles based on the principle of plant photosynthesis.
2.Marking the carbon footprint of textiles is an environmental initiative that the organizer of the Performance Days exhibition has been committed to promoting.
3.Carbon standard certification: Currently, 14 countries and regions around the world have developed 19 product carbon footprint evaluation systems, evaluating over 2,500 products. China Quality Certification Center (CQC) provides carbon footprint services for products in industries such as textiles based on ISO/TS 14067 and PAS 2050 standards.
Bionics
Bionic Function
Bionic Colors
Background
Biomimetics involves numerous research and application fields. In recent decades, the development of biomimetic technology has attracted much attention when combined with textile technology to develop new types of textiles. By applying biomimetic principles, the use of chemicals in production can be reduced, resulting in lower carbon footprints for products.
Application
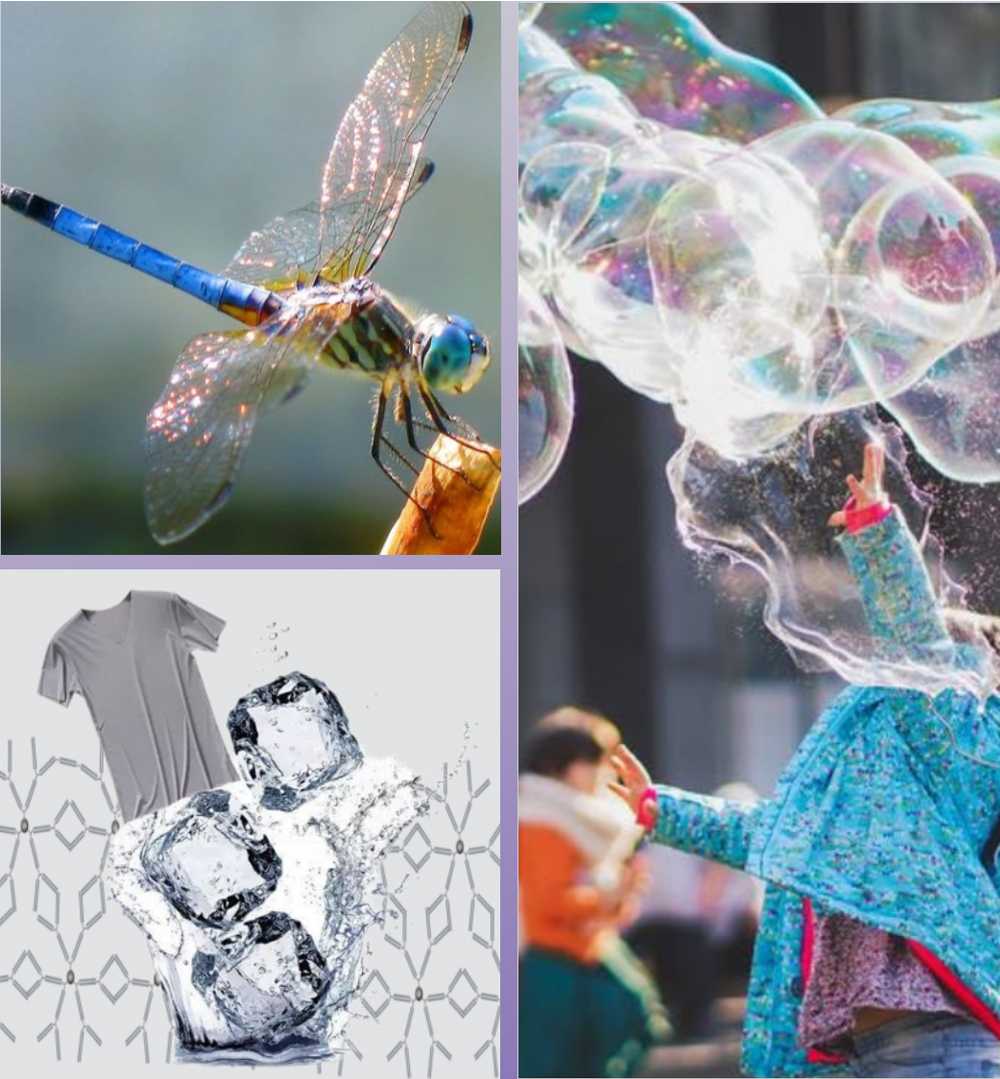
1.Bionic function: In hot and humid environments with intense movement or exposure to sunlight, heat accumulates on the skin's surface, resulting in excessive sweating and potentially causing an imbalance in body temperature and heat stress. Therefore, the development of personal heat and moisture management technologies based on fiber materials has emerged. Using biomimetic principles to simulate the relationship between biological function and structure is considered a promising method for designing temperature control fibers and textiles.
2.Bionic color: While most colors in nature are produced by pigments, known as chemical coloration, some colors are formed by highly subtle microstructures known as structural coloration. These structural colors often have a glossy appearance, and certain colors may even change depending on the viewing angle.

Microbial Technology
Algae fiber
Black algae ink
Plant/Food dyeing
Background
The application of microorganisms in the fashion industry has a history of several decades. After entering 2020, various extreme climates and ecological environment problems have become more and more frequent, making people pay more attention to harmonious coexistence between humans and nature. The technology of using microorganisms with more environmentally friendly properties has gradually received attention and become a growth engine for the future.
Application
1.Algae Lyocell: Algae is processed and injected into cellulose fibers.
2.Black algae ink: The by-product of spirulina is processed by heat treatment and concentrated into black powder, which is used as a pigment and covered on the surface of the fabric by surface scraping technology. This can reduce carbon emissions by replacing petroleum-based carbon black dyes.
3.Microbial Dyeing: Color genes are extracted from animals such as birds and butterflies and inserted into certain bacteria, enabling bacteria to obtain different colors.
4.Mycelium: Bolt Threads and MycoWorks are two of the leading companies in mycelium material development, each having its own patented mycelium cultivation process and finished product manufacturing technology.

Smart Textiles
Passive Intelligent Fiber
Photovoltaic Energy
Intelligent Healthcare
Background
As an industry that has come under strict scrutiny for overuse of natural and fossil resources, the fashion industry can effectively reduce its impact on resources and the environment through the development of new materials using recycling and upcycling techniques. It is important to prioritize the use of regenerated resources within the textile and fashion industry.
Application
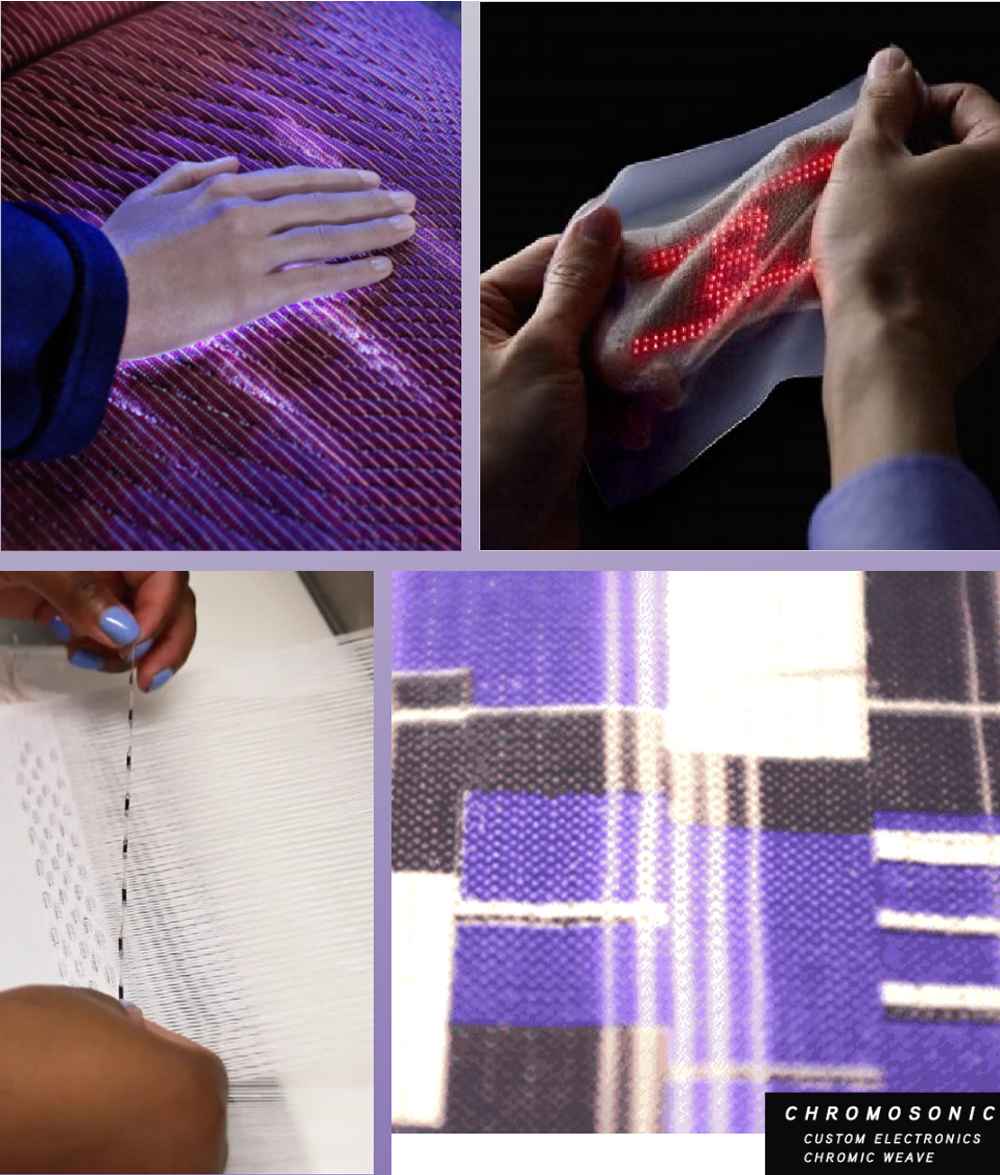
1.Photovoltaic Energy: With the widespread use of wearable technology, smart textiles, and electronic textiles in sports, health, and workwear, all sensors, devices, and visual effects added to textiles require power. Solar cells can replace traditional batteries in some applications, enabling smart textiles to achieve energy independence.
2.Intelligent Healthcare: Currently, the medical smart textile market is mainly divided into two directions: health monitoring and patient protection. According to a Market Research Future research report, the medical smart textile market will show significant growth with a strong compound annual growth rate before 2027.
3.Intelligent Interaction: The emergence of new technologies such as IoT and AI is changing the textile and clothing industry. Currently, the two more mature areas in smart interactive textiles are sensor data transmission and cutting-edge artificial intelligence technologies.


 Inquire(
Inquire(
 HOME
HOME S/S 2024 Sporty Knit Keywords
S/S 2024 Sporty Knit Keywords  You May Also Like
You May Also Like






















 Tel
Tel
 WhatsApp
WhatsApp
 Email
Email
 Address
Address






